 |
|
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) are hematologic malignancies that are characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis. Even though these are preleukemic disorders that can transform to Acute Myeloid Leukemia in a third of cases, most of the morbidity is due to low blood counts. Our lab if focused in studying the molecular pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndromes and identifying targetable pathways in this disease.
We have been involved in study of pathogenesis of myeloid malignancies such as Myeloproliferative neoplasms, MDS and AML. We have elucidated the critical role of signaling pathway (p38 MAP kinase, TGF-beta, smad2/3 and others) activation in MDS and this work has directly led to the therapeutic targeting as these pathways in clinical trials in MDS/AML (JCI 2018, Science TM, 2018, Nat Chem Biol,2015 Blood 2015, 2011). We were one of the first groups to define stem cell alterations in MDS/AML and have optimized flow-cytometric and molecular assays to work with small numbers of primary samples (Nat Med, 2018; Nat Cell Bio, 2019; JCI 2014, Blood 2012). Our lab has also developed genome wide assays for DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation and used them in a variety of tumor models (Can Disc, 2019; JCI, 2018; Gen Res, 2017, NAR 2016, Nat Immunol 2015).
|
Determining the molecular basis of decreased blood counts in myelodysplastic syndromes
We are studying the molecular mechanisms of dysplastic differentiation in MDS. We have demonstrated the role of DOCK4 haploinsufficiency in anemia in MDS with deletions of chromosome 7q. We have demonstrated the potential of p38 MAPK inhibitors in stimulating hematopoiesis in MDS. This discovery led directly to two clinical trials (with SCIO-469 and ARRY-614) that have shown single agent activity in raising blood counts.
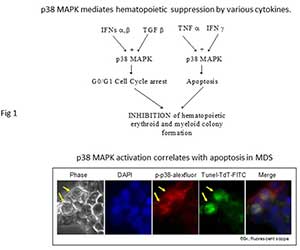
Figure 1 Our laboratory identified that the p38 MAPK is constitutively activated in low grade MDS, mediates progenitor apoptosis in MDS and provides an excellent therapeutic target to stimulate MDS hematopoiesis. We demonstrated that p38 MAPK activation is required for interactions between the marrow stroma and hematopoietic cells that lead to production of myelosuppressive cytokines by the stroma. These studies provided the preclinical rationale for the use of p38 MAPK inhibitors in MDS
Smith M*, Choudhary GS*, Pellagatti A, Choi K, Bhagat TD, Gordon-Mitchell S, Von Ahrens D, Pradhan K, Steeples V , Kim S, Steidl U , Salomonis N, Walter M, Komurov K, Boultwood J*, Verma A*, Starczynowski D*
U2AF1 mutations induce oncogenic innate immune pathways by regulating the expression of active IRAK4 isoforms in hematologic malignancies
Nature Cell Bio 2019, * Equal Contribution
Bhagat TD, Chen S, Bartenstein M, Barlowe AT, Von Ahrens D, Choudhary GS, Tivnan P, Amin E, Marcondes M, Sanders MA, Hoogenboezem RM, Kambhampati S, Ramachandra N, Mantzaris I, Sukrithan V, Laurence R, Lopez R, Bhagat P, Giricz O, Sohal D, Wickrema A, Yeung C, Gritsman K, Aplan P, Hochedlinger K, Yu Y, Pradhan K,
Zhang J, Greally JM, Mukherjee SM, Pellagatti A, Boultwood J, Will B, Steidl U, Raaijmakers MHGP, Deeg HJ, Kharas MG, Verma A Wnt/ß-catenin activation by epigenetically aberrant stroma drives myelodysplastic syndrome Cancer Res Jul, 2017, PMID: 28684528
Sundaravel S, Duggan R, Bhagat TD, Ebenezer D, Liu H, Yu Y, Bartenstein M, Unnikrishnan M, Karmakar S, Liu TC, Torregroza I, Quenon T, Anastasi J, McGraw K, Pellagatti A, Boultwood J, Yajnik V, Artz A, Le Beau M, Steidl U, List A, Evans T*, Verma A*, Wickrema A* (*Co-Corresponding) Reduced DOCK4 Expression Leads to Erythroid Dysplasia in MDS. PNAS. 2015; Nov 17;112(46): PMID: 26578796
Bachegowda L, Morrone K, Winski SL, Mantzaris I, Bartenstein M, Ramachandra N, Giricz O, Sukrithan V, Nwankwo G, Shahnaz S , Bhagat T, Bhattacharyya S, Assal A, Shastri A, Gordon-Mitchell S, Pellagatti A, Boultwood J, Schinke C, Yu Y, Guha C, Rizzi J, Garrus J, Brown S, Wollenberg L, Hogeland G, Wright D, Munson M`, Rodriguez M, Gross S, Chantry D, Zou Y, Platanias L, Burgess LE, Pradhan K, Steidl U, Verma A Pexmetinib: a novel dual inhibitor of Tie-2 and p38 MAPK with efficacy in preclinical models of myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia Cancer Res 2016 Jun 10. PMID: 27287719
Navas T, Mohindru M, Estes M, Ma JY, Sokol L, Pahanish P, Parmar S, Haghnazari E, Zhou L, Collins RC, Kerr I, Nguyen A, Xu Y, Platanias LC, List AA, Higgins LS, Verma A. Inhibition of overactivated p38 MAPK can restore hematopoiesis in myelodysplastic syndrome progenitors Blood 2006, 15;108(13):4170-7 PMID: 16940419 PMCID: PMC1895446
Role of TGF-β / SMAD activation in the pathogenesis of MDS
We demonstrated that TGF-beta family/SMAD2/3 signaling is overactivated and pathogenic in MDS. We showed the potential of TGF-beta receptor I kinase inhibitor, Galunisertib, in this disease; findings that have led to an international multicenter trial that recently finished accrual. Additionally, this work has stimulated other trials using agents that inhibit SMAD2/3 activation in MDS such as Sotanercept and Luspatercept (Luspatercept expected to be FDA approved in 2019). Our lab studies have further shown that TGF-beta-smad signaling is activated in MDS due to reduced levels of negative regulator, SMAD7. Further mechanistic studies have shown that reduction of SMAD7 is mediated by increased levels miR-21, thus providing a molecular map of why stem cells in MDS are sensitized to TGF-beta family ligands and prone to dysplastic hematopoiesis.
Bhagat T, Zhou L, Sokol L, Caceres G, Gundabolu K, Gordon S, Mantzaris I, Gligich O, Yu Y, Bhattacharyya S, Jing X, Polineni R, Tamari R, Bhatia K, Pellagatti A , Boultwood J, Kambhampati S, Steidl U, Stein C, Ju W, Liu G, Kenny P, List A, Bitzer M, Verma A. miR-21 mediates hematopoietic suppression in MDS by activating TGF-b signaling Blood 2013, Apr 11;121(15):2875-81. PMID: 23390194
L Zhou, C McMahon, T Bhagat, C Alencar, Y Yu, M Fazzari, D Sohal, C Heuck, K Gundabolu, C Ng, Y Mo, W Shen, A Wickrema, G Kong, E Friedman, L Sokol, G Mantzaris, A Pellagatti , J Boultwood, LC. Platanias. U Steidl, L Yan, JM Yingling, MM Lahn, A List, M Bitzer and , Verma A Reduced SMAD7 leads to overactivation of TGF-beta signaling in MDS that can be reversed by a specific inhibitor of TGF-beta receptor I kinase. Cancer Research 2011 Feb 1;71(3):955-63.PMID: 21189329
Zhou L, Nguyen AN, Sohal D, Ma JY, Pahanish P, Gundabolu K, Hayman J, Chubak A, Mo Y, Bhagat T, Das B, Haghnazari E, Navas T, Parmar S, Kambhampati S, Pellagati A, Braunchweig I, Zhang YE, Wickrema A, Boultwood J, Platanias LC, Higgins LS, List A, Bitzer M, Verma A. Inhibition of Transforming Growth Factor beta receptor I kinase can stimulate hematopoiesis in Myelodysplasia, Blood 2008 Oct 15;112(8):3434-43 PMID: 18474728
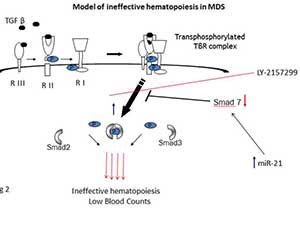 Figure 2
Our lab provided the first comprehensive evidence for TGF-β family / SMAD activation in MDS and defined the functional role of Smad2/3 pathway in hematopoietic suppression in MDS. This work demonstrated that (i) a TGF-β secreting transgenic mouse can serve as a novel model of cytokine-induced bone marrow failure, and (ii) that inhibition of the TGF-β signaling pathway by genetic and pharmacologic means can stimulate in vitro hematopoiesis in MDS. These findings strongly suggest that novel TBRI kinase inhibitors may be clinically useful in the treatment of MDS. Recently we showed that Smad7, an important negative regulator of TBRI kinase, is markedly downregulated in MDS marrow progenitors leading to increased TBRI signaling. They also found that the novel TBRI inhibitor, LY-2157299, shows activity in mouse models of MDS. More recently, we have shown that increased levels of miR-21 are seen in MDS and target SMAD7 in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. This work has shown that inhibiting miR-21 can also reverse TGF-β signaling and stimulate hematopoiesis in MDS.
Figure 2
Our lab provided the first comprehensive evidence for TGF-β family / SMAD activation in MDS and defined the functional role of Smad2/3 pathway in hematopoietic suppression in MDS. This work demonstrated that (i) a TGF-β secreting transgenic mouse can serve as a novel model of cytokine-induced bone marrow failure, and (ii) that inhibition of the TGF-β signaling pathway by genetic and pharmacologic means can stimulate in vitro hematopoiesis in MDS. These findings strongly suggest that novel TBRI kinase inhibitors may be clinically useful in the treatment of MDS. Recently we showed that Smad7, an important negative regulator of TBRI kinase, is markedly downregulated in MDS marrow progenitors leading to increased TBRI signaling. They also found that the novel TBRI inhibitor, LY-2157299, shows activity in mouse models of MDS. More recently, we have shown that increased levels of miR-21 are seen in MDS and target SMAD7 in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. This work has shown that inhibiting miR-21 can also reverse TGF-β signaling and stimulate hematopoiesis in MDS.
Identifying Stem cell alterations and targets in MDS and acute myeloid leukemia
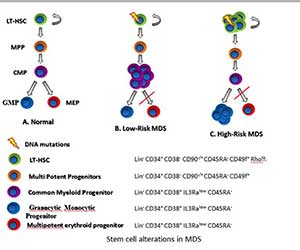
Figure 3In collaboration with the Steidl Lab, we have determined quantitative and qualitative
alterations in stem and progenitor cells in myelodysplastic neoplasms and identification of novel therapeutic targets against aberrant stem cells. Demonstrated that aberrant stem cells persist during morphological remissions and are involved in relapse. Many studies are now being conducted targeting novel stem
cell targets identified in this study. First report of methylome analysis of highly purified human stem cells using nano-HELP assay developed by PI. Demonstrated that stem cell like signature is prognostic in AML and performs better than gene expression based signature.
Chen J, Kao YR, Sun D, Todorova TI, Reynolds D, Narayanagari SR, Montagna C, Will B, Verma A*, Steidl U*. MDS progression to AML at the stem cell level. Nature Medicine. 2019, Jan (*Co-Corresponding) PMID: 30510255
Shastri A, Choudhary G, Teixeira M, Gordon-Mitchell S, Ramachandra N, Bernard L, Bhattacharyya, S. Lopez, R. Pradhan, K. Giricz, O. Ravipati, G. Wong, L. F. Cole, S. Bhagat, T. D. Feld, J. Dhar, Y. Bartenstein, M. Wickrema, A. Ye, B. H. Frank, D. A. Pellagatti, A. Boultwood, J. Zhou, T. Kim, Y. MacLeod, A. R. Epling-Burnette, P. K. Ye, M. McCoon, P. Woessner, R. Steidl, U. Will, B. Verma, A. Antisense STAT3 inhibitor decreases viability of myelodysplastic and leukemic stem cells. J Clin Invest. 2018, PMID: 30252677
Will B, Zhou L, Vogler TO, Ben-Neriah S, Schinke C,Tamari R, Yu Y, Bhagat T, Bhattacharya S, Barreyro L, Heuck C, Mo Y, Parekh S, McMahon C, Pellagatti A, Boultwood J, Montagna C, Silverman L, Maciejewski J, Greally JM, Ye BH, List AF, Steidl C, Steidl U, Verma A. Stem and progenitor cells in
myelodysplastic syndromes show aberrant stage specific expansion and harbor genetic and epigenetic alterations, Blood 2012; 120(10):2076-86. PMID: 22753872
Bartholdy B, Christopeit M, Will B, Mo Y, Barreyro L, Yu Y, Bhagat T, Okoye-Okafor U, Todorova T, Greally J, Levine RL, Melnick A, Verma A.*, Steidl U*. *Co-Corresponding A human hematopoietic stem cell-commitment related DNA cytosine methylation signature is prognostic for overall survival
in acute myeloid leukemia J Clin Investigation 2014Feb 3 PMID: 24487588
Schinke C, Giricz O, Li W, Shastri A, Gordon S, Barreryo L, Bhagat T, Bhattacharyya S, Ramachandra N, Bartenstein M, Pellagatti A, Boultwood J, Wickrema A, Yu Y, Will W, Wei S, Steidl U*, Verma A*. * co-corresponding authors IL8-CXCR2 pathway inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy against MDS and AML stem cells. Blood. 2015, Mar 25. PMID: 25810490
Role of DNA methylation / hydroxymethylation in cancer.
We have defined the role of epigenetic and genetic alterations in MDS and numerous other malignancies. Our lab has developed and optimized the HELP assay to work with small amounts of tumor tissues and has used it to define novel genome wide alterations in DNA methylation in MDS, Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), Esophageal cancer and Renal cell cancer. Recently our lab developed a genome wide assay for a new epigenetic modification, hydroxymethylation, that is now being used in numerous ongoing studies.
Jeong JJ, Gu X, Nie J, Sundaravel S, Liu H, Kuo W, Bhagat TD, Pradhan K, Cao J, Nischal S, McGraw K, Bhattacharyya S, Bishop M, Artz A, Thirman M, Moliterno AR, Ji P, Levine RL, Godley LA, Steidl U, Beiker J, List AF, Saunthararajah Y, He C, Verma A,* Wickrema A*
Cytokine regulated phosphorylation and activation of TET2 by JAK2 in hematopoiesis Cancer Discovery 2019, (In Press) * Equal Contribution
Shenoy S, Bhagat TD, Cheville JC, Lohse C, Bhattacharyya S, Tischer A, Machha V, Gordon-Mitchell S, Choudhary GS, Wong L, Gross L, Ressegue E, Leibovich BC, Boorjian S, Steidl U, Wu X, Pradhan K, Gartrell B, Agarwal B, Pagliaro L, Suzuki M, Greally J, Rakheja D, Thompson R, Susztak K, Witzig T, Zou Y, Verma A Ascorbic acid-induced TET activation mitigates adverse hydroxymethylcystosine loss in renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 2019, Mar 4;130. PMID: 30702441
Bhattacharyya S, Pradhan K, Campbell N, Mazdo J, Vasantkumar A, Maqbool S, Bhagat TD, Gupta S, Suzuki M, Yu Y, Greally JM, Steidl U, Bradner J, Dawlaty M, Godley L, Maitra A, Verma A Altered hydroxymethylation is seen at regulatory regions in pancreatic cancer and regulates oncogenic pathways Genome Res, 2017 Oct 6. PMID: 28986391 (Cover)
Bhattacharyya, Si; Yu, Y; Suzuki, M; Campbell, N; Mazdo, J; Vasantkumar, A; Bhagat, T; Nischal, S; Christopeit, M; Parekh, S; Steidl, U; Godley, L; Maitra, A; Greally, J; Verma, A Genome wide hydroxymethylation tested using the HELP-GT assay shows redistribution in cancer Nucleic Acid Res 2013 Sep 1;41(16) PMID: 23861445 PMCID: PMC3763560
Cimmino L, Dawlaty MM, Ndiaye-Lobry D, Yap YS, Bakogianni S, Yu Y, Bhattacharyya S, Shaknovich R, Geng H, Lobry C, Mullenders J, King B, Trimarchi T, Aranda-Orgilles B, Liu C, Shen S, Verma A, Jaenisch R, Aifantis I. TET1 is a tumor suppressor of hematopoietic malignancy. Nat Immunol. 2015 Apr 13. PMID: 25867473
Molecular outcome studies in WTC first responders and Bronx minority populations
Determining ethnicity specific outcomes in hematologic malignancies: Clinical research using Montefiore databases has shown that different patient outcomes are seen in inner city populations of the Bronx. We have also been conducting studies in early detection of hematologic malignancies in first responder firefighters exposed to the 911 WTC disaster.
Landgren O*, Zeig-Owens R*, Giricz O*, Goldfarb D, Murata K, Thoren K, Ramanathan L, Hultcrantz M, Dogan A, Nwankwo G, Steidl S, Pradhan K, Hall C, Cohen HW, Jaber N, Schwartz T, Crowley L, Crane M, Irby S, Webber MP, Verma A*, Prezant DJ*
Multiple Myeloma and Its Precursor Disease among Firefighters Exposed to the World Trade Center Disaster. JAMA Onc, 2018 Jun 1;4(6):821-827. PMID: 29710195 * Equal Contribution
Shah UA, Chung EY, Giricz O, Pradhan K, Kataoka K, Gordon-Mitchell S, Bhagat TD, Mai Y, Wei Y, Ishida E, Choudhary GS, Joseph A, Rice R, Gitego N, Parrish C, Bartenstein M, Goel S, Mantzaris I, Shastri A, Derman O, Binder A, Gritsman K, Kornblum N, Braunschweig I, Bhagat C, Hall J, Graber A, Ratner L, Wang Y, Ogawa S, Verma A*, Ye BH*, Janakiram M.*
North American ATLL has a distinct mutational and transcriptional profile and responds to epigenetic therapies. Blood. 2018 Aug 13. PMID: 30104217 * Equal Contribution
Darbinyan K, Shastri A, Budhathoki A, Helbig D, Snyder R, Pradhan K, Saleh-Esa J, Kornblum NS, Binder AF, Goel S, Janakiram M, Derman O, Gritsman K, Steidl U, Braunschweig I, Verma A, Mantzaris I. Hispanic ethnicity is associated with younger age at presentation but worse survival in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Advances
3. Mantzaris I, Yu Y, Msaouel P, Lam AP, Janakiram M, Friedman EW, Steidl U, Verma AK. Analysis of overall survival in a large multiethnic cohort reveals absolute neutrophil count of 1,100 as a novel prognostic cutoff in African Americans. Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 18;7(42):67948-67955. PMID:27144332
Goel S, Hall J, Pradhan K, Hirsch C, Przychodzen B, Shastri A, Mantzaris I, Janakiram M, Battini R, Kornblum N, Derman O, Gritsman K, Al-Hafidh J, Wang Y, Halmos B, Steidl U, Maciejewski JP, Braunschweig I, Verma A. High prevalence and allele burden-independent prognostic importance of p53 mutations in an inner-city MDS/AML cohort. Leukemia. 2016 Aug;30(8):1793-5. PMID:27125205
Msaouel P, Lam AP, Gundabolu K, Chrysofakis G, Yu Y, Mantzaris I, Friedman E, Verma A. Abnormal platelet count is an independent predictor of mortality in the elderly and is influenced by ethnicity. Haematologica. 2014 May;99(5):930-6. PMID:2451034013;3(8):e2965 PMID: 18698424